Local Adjustments: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
====Local Contrast & Wavelets - 7==== | ====Local Contrast & Wavelets - 7==== | ||
Local contrast (essentially the same as the global adjustment). | * Local contrast (essentially the same as the global adjustment). | ||
* Wavelets: based on “Wavelet Levels” in the “Advanced” tab with essentially the same features (clarity, contrast, blur…see documentation). Its use in “Local Adjustments” provides additional possibilities such as the removal of large blemishes, grease stains etc. | |||
====CBDL - 2==== | ====CBDL - 2==== | ||
Contrast by detail levels. Can be used to remove sensor or lens marks. | Contrast by detail levels. Can be used to remove sensor or lens marks. | ||
| Line 475: | Line 475: | ||
=====Example: removing multiple spots using wavelet pyramid2===== | =====Example: removing multiple spots using wavelet pyramid2===== | ||
* Looking at the image below, we can see that it is blotchy | * Looking at the image below, we can see that it is blotchy | ||
Revision as of 09:20, 14 September 2020
(12 september 2020)
Introduction
Local editing in RawTherapee is based on RT-spots, which are similar in principle to the U-Point concept originally used in Nikon Capture NX2 © and subsequently in the Nik Collection ©, DxO PhotoLab © and Capture NXD ©. RT-spots use algorithms developed specifically for RawTherapee by Jacques Desmis.
This approach is completely different to the more familiar local editing methods used in applications such as the GIMP, Photoshop © etc., which primarily use selection tools such as lassos, magic wands etc., associated with brushes, layers and blend masks. These methods can be time consuming and difficult to use accurately when complex shapes are involved.
An RT-spot consists of either an ellipse or a rectangle with a variable-diameter spot at the center.
The shapes have four control points, which can be adjusted independently or symmetrically, and future developments will provide enhanced shape manipulation.
The RT-spot algorithm uses shape detection based on ΔE (the change in the visual perception of two given colours) to select the parts of the image to be modified inside the ellipse or rectangle .
The extent to which these modifications are applied can be finely controlled allowing for very precise selections. Further refinement is possible with additional parametric masks but the shape-detection algorithms should be sufficient for the vast majority of local editing requirements.
RT-spots can also be used to exclude the algorithm from influencing certain parts of the image .
The modifications that can be carried out are extensive and incorporate most of the functions available in RawTherapee’s global adjustment tools along with some additional tools available only in the Local Adjustment tab.
The tools are grouped in the following modules (Title - position in pipeline):
Color & Light - 11
Adjust color, lightness, contrast and correct small defects such as red-eye, sensor dust etc. Other functions include a graduated filter, L*a*b* curves and blend modes.
Shadows-Highlights & Tone Equalizer - 5
Adjust shadows & highlights either with shadows & highlights sliders or with a tone equalizer. Can be used instead of, or in conjunction with the Exposure module. Can also be used as a graduated filter.
Vibrance & Warm-Cool - 3
Adjust vibrance (essentially the same as the global adjustment). Carry out the equivalent of a white-balance adjustment using a CIECAM algorithm.
Log Encoding - 0
Adjust under-exposed or high-dynamic-range images using a log-encoded algorithm.
Contrast Attenuator-Dynamic Range Compression & Exposure - 10
Modify exposure in L*a*b* space using Laplacian PDE algorithms to take into account dE and minimize artifacts.
Common Color Mask - 13
A tool in its own right. Can be used to adjust the image appearance (chrominance, luminance, contrast) and texture as a function of Scope.
Soft Light & Original Retinex - 6
Apply a Soft-light blend (identical to the global adjustment). Carry out dodge and burn using the original Retinex algorithm.
Blur-Grain & Denoise - 1
Can be used to blur backgrounds, soften skin, add film grain and denoise.
Tone Mapping - 4
Same as the tone mapping tool in the main menu. The main menu tool must be de-activated if this tool is used.
Dehaze & Retinex - 9
Dehaze and Retinex (Advanced mode only). Useful for dehaze, local contrast with high values and simulation of ‘clarity’.
Sharpening - 8
Uses RL deconvolution sharpening. View at 1:1
Local Contrast & Wavelets - 7
- Local contrast (essentially the same as the global adjustment).
- Wavelets: based on “Wavelet Levels” in the “Advanced” tab with essentially the same features (clarity, contrast, blur…see documentation). Its use in “Local Adjustments” provides additional possibilities such as the removal of large blemishes, grease stains etc.
CBDL - 2
Contrast by detail levels. Can be used to remove sensor or lens marks.
Each tool module can be toggled between Basic, Standard & Advanced modes. The default mode can be set in RawTherapee’s Preferences window.
Getting start
Activating local adjustments
- In the tab bar, select the "hand" icon (Local Adjustments tab)
- Turn on the "Local Adjustments" power button (if it is not already activated) and expand the "Settings” module.
- Select "Add"
Preparation
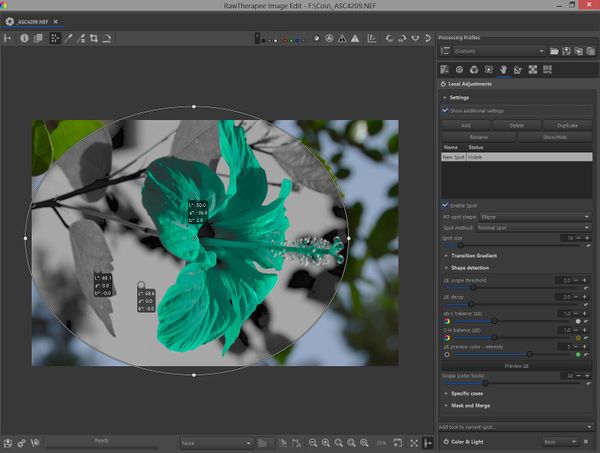
Position the RT-spot at the desired location. In this case, we want to increase the saturation of the red flower and reduce the luminance (lightness) without affecting the rest of the image:
- Move the center of the RT-spot so that it is located on an area representative of what you want to change.
- Position the 4 delimiters well beyond the flower.
- Select the "Lockable Color Picker" and locate 3 colors: a) one on the red flower, b) one on the blue sky, c) one on a green leaf.
- In the example the 3 colors are:
- red flower L=48.6 a=74.4 b=47.0
- blue sky : L=68.6 a=-3.1 b=-16.6
- green leaf : L=48.3 a=-28.3 b=51.4
Raw file: [1]
Adding the Color & Light tool
In the settings menu, choose "Add tool to current spot".
- You will see a list of choices : "Color & Light - 11",..., "Log Encoding – 0" etc.. For each RT-spot you can associate 1 or more tools from the list. The processing order in the pipeline corresponds to the number at the end of the tool description : "Log Encoding - 0" is first (if it is activated), "Color & Light -11" is the last one. This is also the case for the associated masks.
- Select "Color&Light (Defects) - 11"
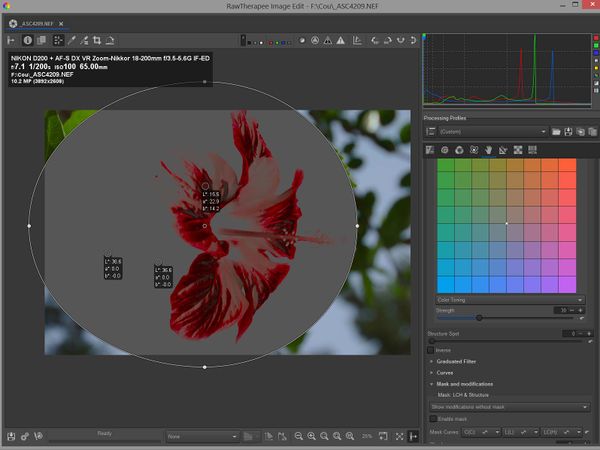
Adjusting luminance (lightness) and chrominance
- Set "Lightness" to -70
- Set "Chrominance" to 130
- Review the results
- The red flower now has a new color L= 41.0, a = 65.6, b = 52.8
- the sky is unchanged
- the green leaf is unchanged
Color Tool Scope and Transition Value
In the "Settings" module
- Observe the effect of moving the "Scope (color tools)" slider
- if you reduce the value (default 30) only a part of the reds will be affected.
- if you increase the value, the sky, then the green leaf, then the whole image will be taken into account (Scope=100)
Leave the Scope value at 100 and in the "Settings" module select "Show additional settings"
- Observe the effect of moving the "Transition value" slider:
- reduce the value to 5
- increase the value to 100 and see the result
Previewing the adjustment area using deltaE - ΔE
You can preview the areas of the image that will be affected by any changes. The preview does not show the changes themselves or the transitions, but allows you to set the scope of any adjustments. There are two possibilities:
- Use the "Preview ΔE" button located in "Settings". This will only work if you have activated one (and only one) of the tools in "Add tool to current spot" menu.
- Use the "Preview ΔE" option in the "Mask and modifications" menu associated with a particular tool (standard and advanced modes only). In this case the GUI takes into account any adjustments made with the tool and works regardless of the number of activated tools.
You can vary the intensity and color of this preview with "ΔE preview color " in the "Shape detection" section of the "Settings" module . The preview will also let you see the effect of varying the other sliders in the Shape detection section.
Viewing the changes
To see the changes :
- Go to "Mask and modifications" > "Show modifications without mask".
- You can visualize the effects of any changes to luminance, contrast, color and saturation, as well as any changes to the texture or structure of the image.
- You can also visualize the incidence of the transition settings:
- "Transition value": percentage of the area that will receive the full effect of any adjustments before dropping off to zero.
- "Transition decay": the rate with which the zone of action decreases
- "Transition differentiation XY": difference in coverage between abscissa and ordinate
Try out the following and observe the effect:
- Change the Scope (color tools). Remember that the Scope slider acts on deltaE
- Transition settings
- Tool settings (luminance, chroma, etc.)
Work on the overall image using an "excluding" spot
Local adjustments are not limited to local touch-ups. You can also use the Local Adjustment tools to process the entire image. Currently you have to expand a rectangular spot manually to cover the image completely but this will be done automatically in future versions.
In "Settings" enable "Show additional settings":
- Set the "RT-spot shape" to a rectangle
- Position the 4 delimiters outside of the preview
- Set the transition to 100 (or another value if you wish to generate a gradient, bearing in mind that there are other tools for making gradients). You are now ready to use all the tools in full image mode
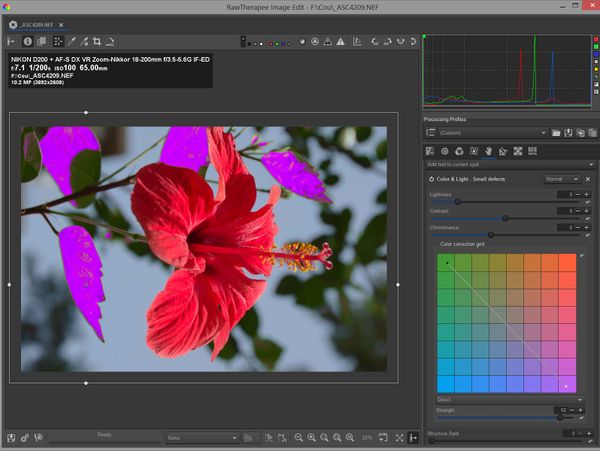
Example: changing the color of the green leaves, except for one
Changing the color of the leaves
- The use of the "a" and "b" components of "Lab" in the "Color correction grid ", by choosing "direct" and a high value of "Strength", leads to a color change of all the leaves.
- You can adjust if necessary with "Scope (color tools)".
- The other colors in the flower, sky etc., are not modified.
Restoring the green color to one of the leaves
- Add a second RT-spot ("Add" in the "Settings" module)
- Choose "Spot Method” = "Excluding Spot”
- Move the RT-spot to the leaf to be changed and expand the spot well beyond the edges of the leaf.
- Adjust "Scope” (under the "Excluding" heading in "Settings") until you get the desired effect.
- If you wish, you can use the "Excluding" spot in the same way as a normal RT-spot and add tools such as Denoise, Blur, etc.
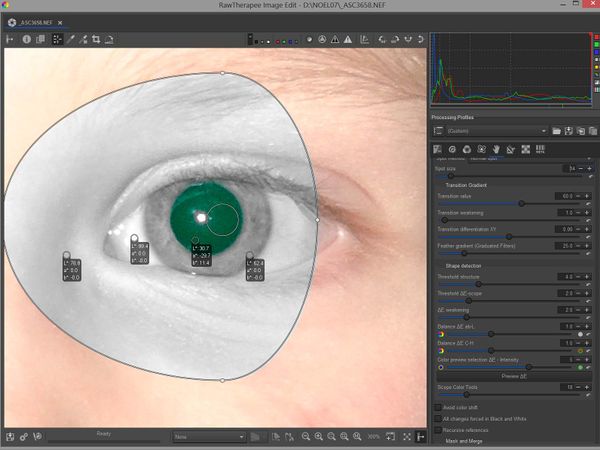
Correcting red eye and removing sensor defects
3 steps: preparation, RT-spot adjustment, red eye removal
Preparation
- Choose a wide selection around the eye
- Put the RT-spot on the red area of the eye (pupil)
- Set 4 "Lockable color pickers" so that you can see the changes
Adjusting the RT-spot
- Add the "Color and Light" tool
- Press the "Preview deltaE" button in "Settings" .
- Adjust the RT-spot to obtain the desired level of selection.
- here we have chosen to reduce the spot size = 14
- "Scope (color tools)" = 18
Removing the red color
- In the "Color and Light" tool, reduce the chrominance to -100
- Observe the result :
- the pupil of the eye has almost no dominant color anymore
- the iris, cornea and facial skin are unchanged
- you may need to change the "Transition value" (lower it) and "Transition decay" (increase it) in "Settings" depending on the case.
Removing sensor defects or spots
The principle is the same as above for removing small sensor faults but in this example we will use different tools
- Either CBDL (Contrast By Detail Levels),
- Or Wavelet pyramid2 - Contrast by levels (Advanced).
- In both cases, reduce the contrast for the lower levels of decomposition
- Adjust "Blur levels” if necessary (wavelet pyramid1)
- Use a low "Transition value" (less than 20) and high "Transition decay" (greater than 15).
- The minimum size of the RT-spot for the CBDL and Wavelet pyramid2 decomposition to function is 32x32 pixels. There are workarounds such as the use of transitions and deltaE to deal with defects smaller than the spot.
Example: removing multiple spots using wavelet pyramid2
- Looking at the image below, we can see that it is blotchy
- A possible solution
- Activate the tool "Local Contrast & Wavelets".
- Choose "Advanced" in the first combobox and then "Wavelet" in the second combobox.
- Adjust “Scope” to 20
- Go to Pyramid2 and activate "Contrast by level".
- Set high values of "Attenuation Response", "Offset" and "Chroma levels" (if necessary)
- Activate the "Contrast by level" curve and reduce the contrast for the lower levels.